Global Production Forecasts
Report: Regional resilience despite volatility for automotive production

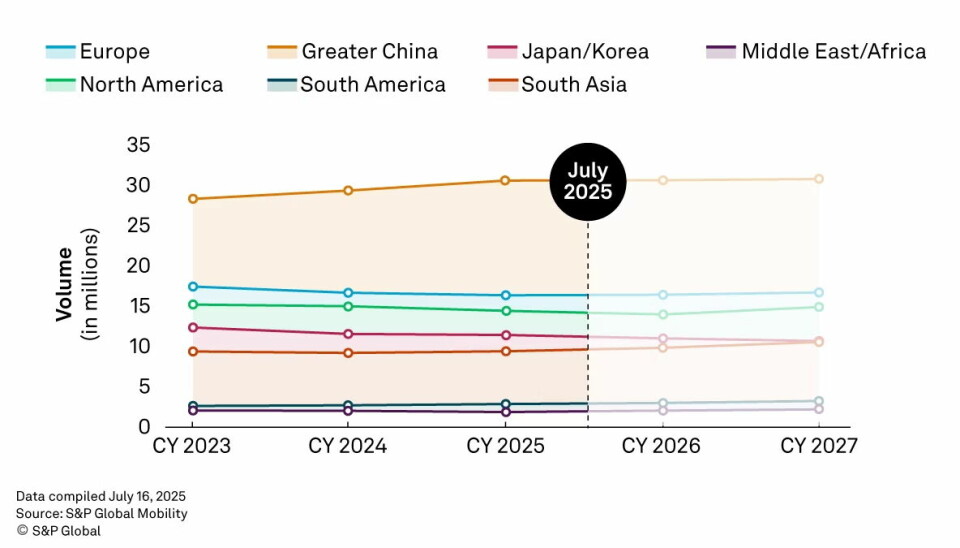
The S&P Global Mobility July 2025 forecast highlights regional resilience and challenges in light vehicle production. Despite volatile trade, North America and Greater China show surprising strength, as other regions seek to recalibrate.
Global automotive production continues to find itself in an intricate dance with international trade dynamics. United States trade policies, notably the persistent exemptions for United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement-compliant (USMCA) parts, remain a key (and apparently indefatigable) influence on global manufacturing.
Yet, the S&P Global Mobility Light Vehicle Production Forecast for July 2025, calmly points to an underlying expectation: a gradual unwinding of tariffs, slated to begin in 2026. This anticipated shift could now unburden the highly-competitive production environment and re-architect global supply chains.
The July forecast presents a complex picture of regional variations, each shaped by the intricate interplay of evolving trade policies and distinct market forces
However, even the most robust forecasts carry unstated risks. The potential for Chinese export restrictions on rare earth elements - vital for electric vehicle (EV) production - represents a significant - though as yet, unquantified - concern. Crucially, a potentially major shortcoming of S&P Global's current projections is that they do not explicitly factor in this potential disruption. They are essentially assuming a smooth, uninterrupted supply of rare earths for EVs and automotive production projects.
Still, shortcomings aside, the report reveals a glimmer of hope for global vehicle manufacturers...
Despite considerable headwinds, this newest forecasts reveal areas of distinct resilience. North America and Greater China, in particular, show unexpected strength, with their production outlooks revised upwards. This buoyancy is an indication of (though capricious), sustained vehicle sales and robust supply chains. The July forecast presents a complex picture of regional variations, each shaped by the intricate interplay of evolving trade policies and distinct market forces.
European production shows measured advance despite inventory tides
Europe's light vehicle production outlook has enjoyed a welcome fillip, registering an increase of 90,000 units for 2025 and a further 55,000 for 2026. These upward revisions are a direct testament to recent production figures that have, against some expectations, outstripped prior estimates. However, this positive trajectory is tempered by a pragmatic recognition of market realities.
According to S&P Global, the latter half of 2025 is expected to witness strategic inventory reductions, a direct consequence of a somewhat subdued demand climate across the continent. Looking further ahead, the improved outlook for 2026 is particularly pronounced for internal combustion engine-based (ICE) vehicles.
This suggests a tenacious, if evolving, role for traditional powertrains, influenced by both updated Clean Air For Europe (EU CAFE) regulations and the anticipated easing of US tariffs. Europe's vehicle manufacturers seem to be demonstrating an impressive capacity for adaptation, adeptly balancing immediate production and market demands with longer-term strategic recalibrations.
Greater China's electric surge
The forecast for Greater China's light vehicle production has undergone a substantial upward revision: 164,000 units for 2025 and an additional 148,000 for 2026, according to the report. This impressive growth trajectory is unequivocally buoyed by a potent combination of proactive government incentives and an inherently dynamic domestic production ecosystem. Too add some shading to this outline, the structural advantage that Chinese auto producers have over their Western counterparts exists both at an organisational, as well as institutional level. The country's enhanced approach to Design For Manufacture (DFM); synthesising production, R&D, engineering and design processes from the outset, endows it with a marked advantage and indubitably contributes to its manufacturing prowess.
The region's 'new energy' vehicle market is not merely expanding, but undergoing a transformation in the true sense of the term, with local brands decisively seizing the reins of innovation and market leadership.
And such assertive domestic prowess - while a major catalyst for regional innovation - simultaneously presents a formidable gauntlet for foreign automakers, who find themselves navigating an intensely competitive and often nationally protective landscape.
Such protectionism, as we know, can have unwanted effects for all stakeholders involved. However, according to S&P, the growing optimism for 2026 production is further fuelled by the expectation of extended subsidies and a generally positive demand outlook, cementing Greater China's undeniable importance in shaping the global automotive narrative.
Asia's contradictory currents: hybrid exports and tariff realities for Japan and Korea
Japan, also, has production forecasts which have experienced a modest, yet still significant uplift: 23,000 units for 2025 and 34,000 projected for 2026. This positive adjustment stands largely as a testament to Toyota's astute strategy of expanding its full-hybrid exports, highlighting a keenly identified growth area that cleverly leverages existing technological strengths.
And the country has just received another boost, likely to push up S&P Global's projection of 34,000 units for 2026. Today's (July 24) confirmed trade agreement between the United States and Japan, reduces US tariffs on Japanese auto imports to 15 percent from a previously threatened 25 percent, providing substantial relief to Japanese automakers. The swift development significantly enhances their competitive position in a crucial market - at a crucial time - immediately boosting investor sentiment and potentially influencing future production strategies.
Similarly, South Korea's production outlook for 2025 has been increased by 36,000 units, a reflection of both improved domestic stability, and export performance that surpassed initial expectations.
Yet, the longer-term view for South Korea, says S&P, specifically for 2026 and 2027, remains conspicuously static. This persistent projection is directly linked to the anticipated impacts of US tariffs, demonstrating how deeply entrenched trade policies can dictate national manufacturing strategies. The region, therefore, offers a compelling dual narrative: focused growth in specific segment, tempered by the pervasive pressures of external trade.
North America's rush for resilience and 'the BEV reset'
North America's light vehicle production outlook has received a substantial uplift of 241,000 units for 2025, a figure that calls attention to the region's remarkable resilience despite persistently volatile tariff policies. Yet, this short-term gain is counterbalanced by a reduction in projections for 2026 and 2027.
The recalibration grows out of a natural inventory stabilisation following recent surges, and the lingering, often unpronounced, effects of those same tariff impacts. Within this broader canvas, the EV production segment in North America is poised for particular volatility.
This is largely driven by ongoing shifts in both subsidy and emissions policies, which are in turn, leading to a tangible reduction in the outlook for dedicated battery electric vehicle (BEV) production. Manufacturers in the region face the critical imperative of rapidly adapting their strategies to an ever-morphing regulatory and incentive environment.
South America's economic rebalancing act and Brazil's tax catalyst
The outlook for South America's light vehicle production has been revised upwards by 56,000 units for 2025. Another gain. According to the report, this positive uptick is primarily attributable to the implementation of a new taxation regime in Brazil. This new framework is widely expected to bolster competitiveness and enhance environmental criteria, promising a significant - potentially transformative - boost to Brazil's domestic output.
Conversely, Argentina's production is projected to decline. This is interpreted as a direct consequence of the combined effects of Brazil's new tax regime and the dynamics of import flows, which are collectively impacting demand for locally manufactured models. Such regional divergence points to the fact that national economic policies can create distinct, and sometimes conflicting, outcomes for automotive manufacturing across the continent.
South Asia and ASEAN navigate economic crosscurrents
The light vehicle production forecast for South Asia has seen a marginal increase for 2025, but this is followed by a subsequent reduction for both 2026 and 2027. This nuanced adjustment emerges from broader economic uncertainties that continue to ripple through the region's manufacturing infrastructure. The ASEAN market, however, particularly stands out with an upward revision of 22,000 units, propelled by robust export momentum.
Lastly, we find that India's automotive production outlook remains notably subdued, grappling with scheduled maintenance shutdowns and necessary inventory corrections among automakers. The overarching concern regarding rare earth materials continues to be a closely-watched factor, as potential supply chain risks in this critical area could still significantly impact vehicle production across the South Asia region, presenting an ongoing, and difficult challenge for manufacturers.






