Volkswagen accelerates AI-powered production with 5-year AWS extension
The platform now hosts more than 1,200 AI-driven applications, ranging from real-time image-based quality inspections to energy optimisation, with machine learning executed via AWS services such as Amazon SageMaker.
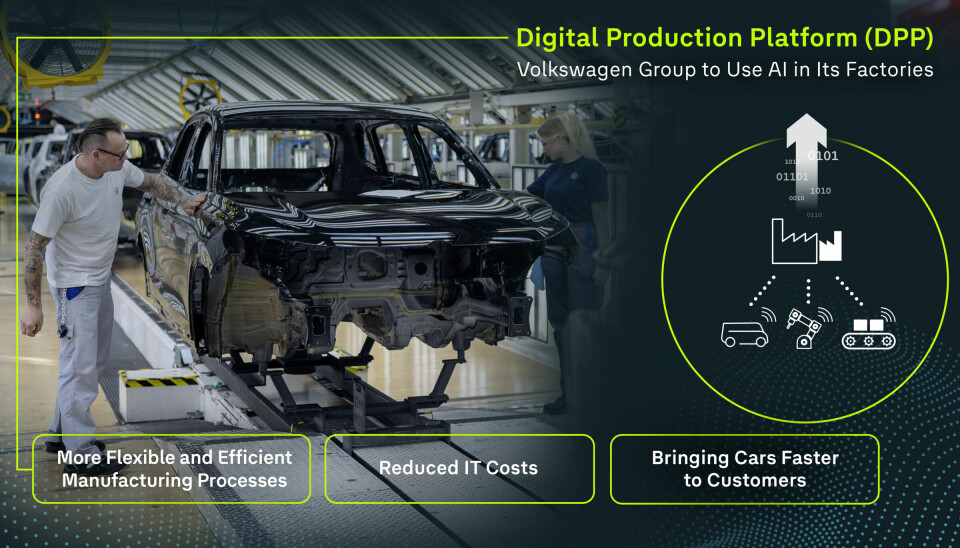
Volkswagen Group has confirmed a five-year extension of its strategic partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS), solidifying the Digital Production Platform (DPP), often dubbed the "factory cloud", as the digital backbone powering its manufacturing transformation.
Already live at 43 plants spanning Europe, North America, and South America, the DPP is scaling AI, computer vision, simulation, and cloud orchestration across Volkswagen’s global footprint. It connects order intake, logistics, and assembly lines, enabling uniform rollout of IT systems across plants.
While exact figures remain internal, Volkswagen has publicly cited "medium-term savings in the double-digit million-euro range" driven by efficiencies from DPP‑enabled digitalisation and streamlined operations.
A smart factory at scale
The platform now hosts more than 1,200 AI-driven applications, ranging from real-time image-based quality inspections to energy optimisation, with machine learning executed via AWS services such as Amazon SageMaker.
"The DPP is the digital nervous system of our factories and the key to a future of AI-powered production."
At its Poznań facility, one AI application has already cut electricity consumption by 12% and reduced CO₂ emissions, demonstrating rapid payback from intelligent analytics.
Continuity and evolution
Back in 2019, AMS first noted Volkswagen’s Industrial Cloud initiative highlighting its intent to replace the "spaghetti architecture" of hundreds of incompatible systems with a unified, reusable software stack across all plants.
Since then, the DPP has become a launchpad for digital use cases, as multiple AI-driven tools are deployed for predictive maintenance, digital twin orchestration, and logistics optimisation.
At AMS’s Automotive Evolution North America 2024 event, Chris Glover, former EVP for Chattanooga Operations at Volkswagen Group of America highlighted the DPP's role in standardising manufacturing technologies.
“Our lines are controlled and monitored by complex computer systems, and supported by other technologies such as RFID tagging, pick‑to‑light, AGVs and vision control systems," he said. "Our Digital Production Platform helps us leverage and standardise data and apps across locations.”
Why it matters now
By decentralising AI deployment through the DPP’s MLOps framework, Volkswagen can roll out new production apps up to twice as fast and share improvements seamlessly across continents.
This infrastructure enables faster, scalable deployment of machine learning applications up to 2–3x quicker than earlier methods while maintaining enterprise-grade security, scalability, and governance. Pre-DPP, model deployments required months and involved duplicative work across plants.
Volkswagen is already aligning the DPP with its broader move toward software-defined vehicle (SDV) architecture. AI tools and data frameworks like KI4UPS are being adapted for next-gen electronics systems, especially in collaboration with VW’s Rivian-powered software venture.
By embedding visibility and AI workflows into production, Volkswagen gains a dynamic, cost-efficient, and resilient manufacturing foundation.



